mirror of
https://gitlab.com/magicalsoup/Highschool.git
synced 2025-10-22 11:11:36 -04:00
18 KiB
18 KiB
Unit 2: Chemistry
Chemistry Vocabulary List
| Word | Definition (or diagram/translation) |
|---|---|
| Particle Theory of Matter | Theory that describes the composition and behaviour of matter as being composed of small particles with empty space |
| Matter | Substance that has mass and occupies space |
| Mechanical Mixture | A heterogeneous mixture which one can physically separate |
| Suspension | A heterogeneous mixture where insoluble solid particles are distributed throughout a fluid, floating freely/td> |
| Alloy | A combination of 2+ metals |
| Mixture | A substance that is made up of at least 2 types of particles |
| Qualitative property | A property of a substance that is not measured and doesn’t have a numerical value, such as colour, odour, and texture |
| Qualitative observation | An numerical observation |
| Precipitate | A solid that separates from a solution |
| Density | A measure of how much mass is contained in a given unit volume of a substance; calculated by dividing the mass of a sample of its volume (mass/volume) |
| Element | Element An element is made up of the same atoms throughout, and cannot be broken down further |
| Metal | a solid material that is typically hard, shiny, malleable, fusible, and ductile, with good electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Pure substance | A substance that is made up of only one type of particle |
| Atom | The smallest unit of matter found in substances |
| Solution | A uniform mixture of 2 or more substances |
| Colloid | is substance with small particles suspended in it, unable to be separated by gravity |
| Emulsion | A mixture of 2 insoluble liquids, in which one liquid is suspended in the other |
| Physical Property | Characteristic of a substance that can be determined without changing the makeup of the substance |
| Characteristic | A physical property that is unique to a substance and can be used to identify the substance |
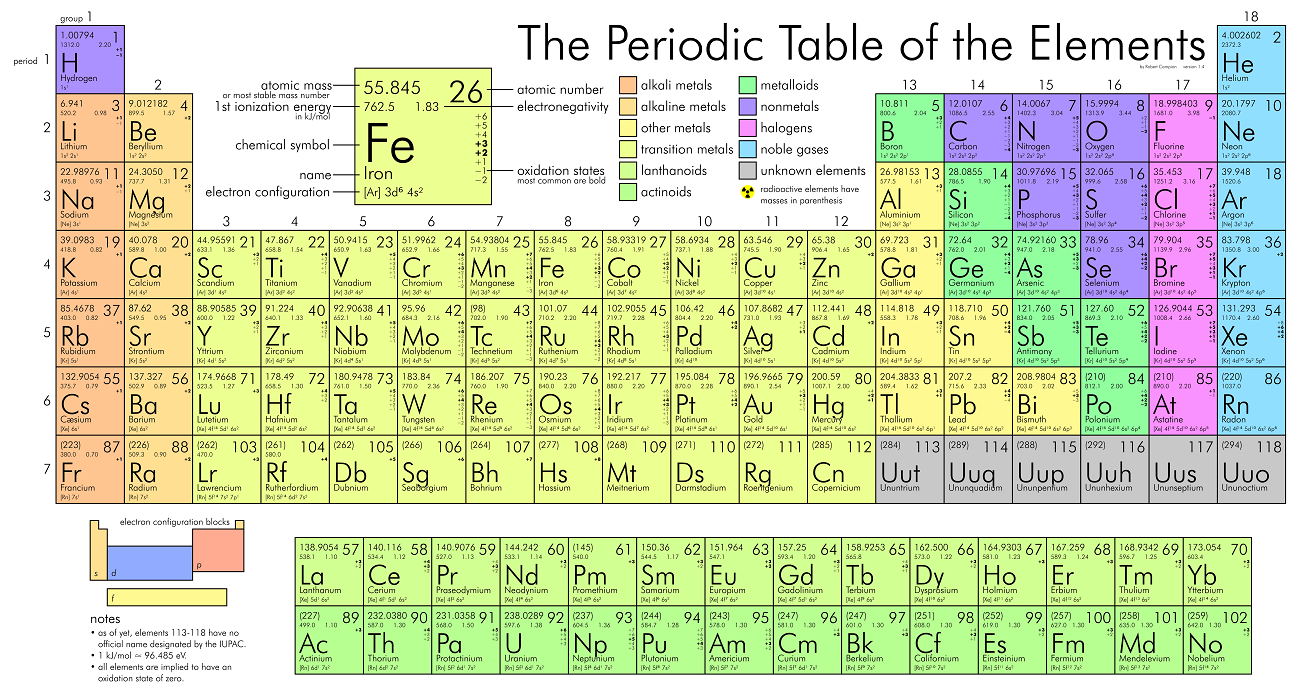
| Periodic Table | a table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns. |
| Compound | Compounds are chemically joined atoms of different elements |
| Non-Metal | A substance that isn’t a metal |
| Physical Change | A change in which the composition of the substance remains unaltered and no new substances are produced |
| Chemical Change |
A change in the starting substance and the production of ONE
or more new substances Original substance does not disappear BUT the composition is rearranged |
| Molecule | Two or more non-metal atoms joined together |
| Diatomic Molecules |
Molecules that only consists of 2 elements H O F BR I N C L - hyrodgen, oxygen, fluorine, bromine, iodine, nitrogen, chlorine. |
| Ions | A Charged particle, that results from a loss (cation - positve, less electrons) or gain (anion - negative, more electrons) of electrons when bonding |
| Electron | Negatively Charged |
| Proton | Positively Charged |
| Neutron | Neutral Charged |
| Ionic Charge | The sum of the positive and negative charges in a ion |
| Covalent Bond | The sharing of electrons between atoms when bonding |
| Valence Electrons | Number of electrons on the most outer orbit/shell of the element |
Particle Theory of Matter
- Matter is made up of tiny particles.
- Particles of Matter are in constant motion.
- Particles of Matter are held together by very strong electrical forces.
- There are empty spaces between the particles of matter that are very large compared to the particles themselves.
- Each substance has unique particles that are different from the particles of other substances.
Physical Properties
- A characeristic of a substance that can be determined without changing the composition (“make-up”) of that substance
- Characteristics can be determinded using your 5 senses and measuring
instruments
- smell, taste, touch, hearing, sight
- scales, tape, measuring meter
The 3 States Of Matter
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| - Holds Shape - Fixed Volume |
- Shape of Container - Free Surface - Fixed Volume |
- Shape of Container - Volume of Container |
Qualitative and Quantitative Properties
| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative Property | A property that IS measured and has
a numerical value |
Ex.
Temperature, height, mass, density |
| Qualitative Property | A property that is NOT measured and has
no numerical value |
Ex.
Colour, odor, texture |
Density
- The amount of mass (or matter) in a certain volume
- It is a quantative physical property
- For any given substance, density is a characteristic physical property.
Sinking Or Floating?
- Most solids are more dense than liquids (except water!)
- When you place a solid object inside a liquid
- It will sink if the object is more dense than the liquid
- It will float if the object is less dense than the liquid
Strange Behaviour of Water
- Its clear, odourless, tasteless, freezes at OoC, boils at 100oC
Its solid form floats on its liquid form!Water particles are different- Due to their
shapeand the way in which theparticlesare arranged, forces it to take upmore spacewhen packed. - Its density is the highest at 4oC, where its in liquid form.
Graphs
- To calculate the density on a graph, simply find the slope of any 2 points on the line in the graph
Quantitative Physical Properties
Density: amount ofstuff(or mass) per unit volume (g/cm3)Freezing Point: point where water solidifies (0oC)Melting Point: point where water liquefies (0oC)Boiling Point: point where liquid phase becomes gaseous (100oC)
Common Qualitative Physical Properties
| Type | Definition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Lustre | Shininess of dullness Referred to as high or low lustre depending on the shininess |
|
| Clarity | The ability to allow light through | Transparent (Glass)
Translucent (Frosted Glass) Opaque
(Brick) |
| Brittleness | Breakability or flexibility Glass would be considered as brittle whereas slime/clay are flexible |
|
| Viscosity | The ability of a liquid or gas to resist
flow or not pour readily through Refer to as more or less viscous |
Molasses is more viscous, water is less (gases tend to get”thicker as heated; liquids get runnier) |
| Hardness | The relative ability to scratch or be
scratched by another substance Referred to as high or low level of hardness |
Can use a scale (1 is wax, 10 is diamond) |
| Malleability | the ability of a substance
to be hammered into a thinner sheet or molded |
Silver is malleable Play dough/pizza dough is less glass is not malleable |
| Ductility | the ability of a substance to be pulled into a finer strand | Pieces of copper can be drawn into thin wires, ductile |
| Electrical Conductivity | The ability of a substance to allow
electric current to pass through it Refer to as high and low conductivity |
Copper wires have high conductivity Plastic has no conductivity |
| Form: Crystalline Solid | Have their particles arranged in an orderly geometric pattern | Salt and Diamonods |
| Form: Amorphous Solid | Have their particles randomly distributed without any long-range-pattern | Plastic, Glass, Charcoal |
Chemical Property
- A characteristic (property) of a substance that describes its
ability to undergo
changes to its composition to produce one of more new substances. AKA BEHAVIOUR. Everything has one! Cannot be determined by physical properties- E.g. ability of nails /cars to rust
- Fireworks are explosive
- Denim is resistant to soap, but is combustible
- Baking soda reacts with vinegar and cake ingredients to rise
- Bacterial cultures convert milk to cheese, grapes to wine, cocoa to chocolate
- CLR used to clean kettles, showerheads because it breaks down minerals
- Silver cleaner for tarnished jewellery, dishes because silver reacts with air to turn black.
Five Aspects Of Chemical Change
Properties Of Metals And Non-Metals
Periodic Table
Trends On The Periodic Table
- The first column are the
Alkali metals.- They are shiny, have the consitency of clay, and are easily cut with a knife.
- They are the most reactive metals.
- They react violently with water.
- Alkali metals are never found as free elements in nature. They are always bonded with another element.
- The second column are the
Alkaline earth metals.- They are never found uncombined in nature.
- The last column are the
Noble gases.- Extremely un-reactive.
- The second last column are the
Halogens.- The most reactive non-metals
- They react with alkali metals to form salts.
- The middle parts are the
transition metals.- They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
- Usually bright coloured.
- They have properties similar to elements in their same family
- Many of them combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.
- The rows outside the table are the
Inner tranistion metals.
- The left to the staircase are the
metals and the right are the non-metals. The ones
touching the staircase are the
metalloids.
How To Read An Element
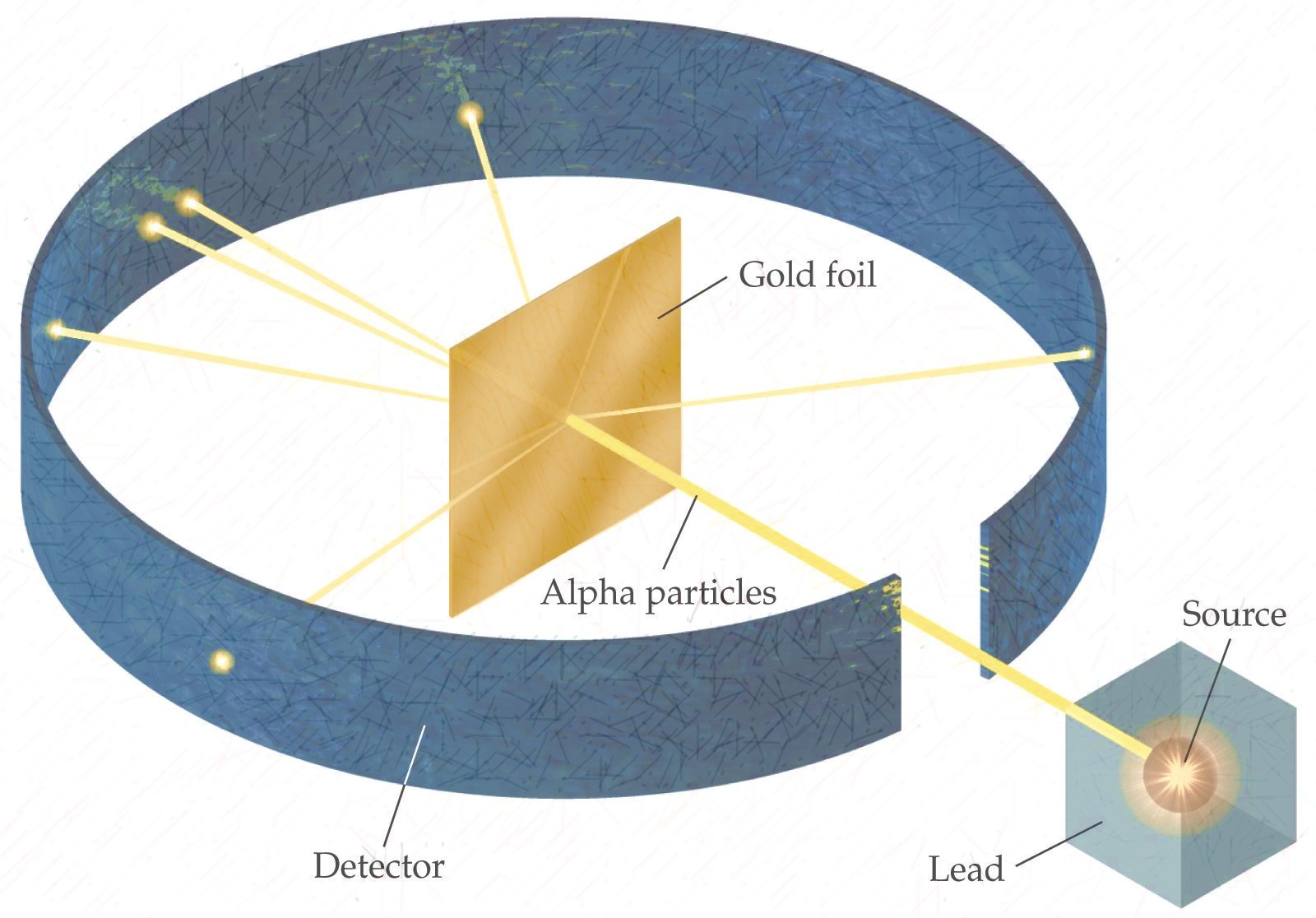
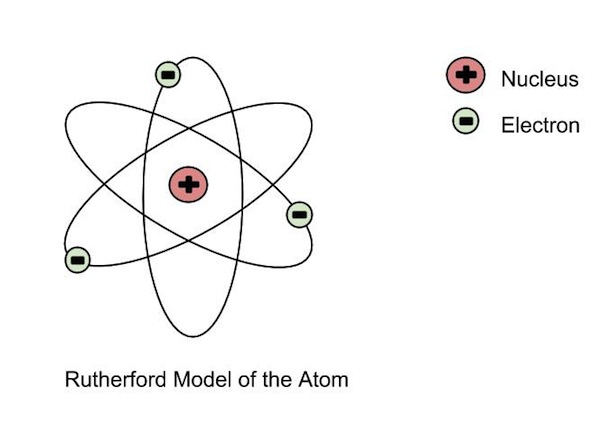
History of The Atom
Carbon
Atoms
- Subscripts - tells us how many of the atom are there, for example N2 means there are 2 nitrongen atoms.
- Use distrubutive property if there are brackets and a subscript, for example, (CO)2 is equilivant to C2O2.
- Atoms are stable if they have a full valence shell (noble gases)
- Each family has the same amount of valence electrons as their family
number, so
alkali metalswould have 1 valence electron,alkaline earth metalswill have 2,halogens will have7 andnoble gaseswould have 8. - They will also have the same amount of protons as their
atomic number. - Number of protons = Number of electrons.
- Number of neutrons = mass - atomic number/number of protons.
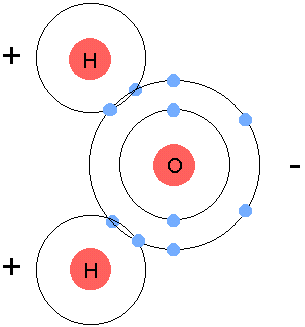
Bohr-Rutherford / Lewis-Dot Diagrams
- Bohr-Rutherford
- Lewis-Dot Diagrams
Bonding
- To combine 2 atoms, each element wants to be stable. So they each want a full valence shell, (outer shell) so they are stable.
- They can either
gain,loseorshareelectrons in order to become stable. - Example:
- Use arrows to show gaining or losing electrons.
- Circle to show sharing of electrons.
Naming of Ionic Bonds
- Write cation (metal) first
- Write anion (non-metal) second
- Change the ending of the non-metal to
ide.
Decomposition
- A chemical change used to break compounds down into simpler substances
- Energy must be ADDED
- Using electricity
- Adding thermal energy
Catalyst
- Substance that accelerates a chemical change without being consumed OR changed itself
Uses of Hydrogen Peroxide
- On cuts/scraps
- Blood has a catalyst = see bubbling O2
- Cleans contact lenses
- Bubbling removes dirt
- Bleaches
- React with compounds that provide color
- RESULT = no colour (bleach blond hair/teeth)